When we look around today, in many devices we use, and in numerous details we see or might not notice, welding processing has actually taken place. From assembling robust chassis parts for the safety of our cars, joining structural elements for the durability of our homes, assembling and maintaining precision machinery for the productivity of industrial plants, from shipbuilding to aircraft production, from the construction industry to power plants, welding plays a vital role in many areas.

This important manufacturing process refers to the process of joining metals or other materials together and is one of the cornerstones of the modern industrial world. Welding process is used for joining, repairing, shaping, or restructuring parts. Combined with advanced technology and expertise, this process is used to stabilise structures, assemble machinery and bring designs to life.
The accuracy and quality of the welding process play a crucial role in the durability of the resulting product. For example, when we consider pressure tanks, the main common feature of this equipment is that they store large amounts of potential energy. A welding error or weak point in the manufacture of a tank will result in the tank suddenly exploding and releasing all its energy, causing perhaps irreversible losses for businesses. For these and other reasons, various control methods and tests such as NDT (non-destructive testing), X-ray examinations and ultrasonic tests are applied to ensure the quality and durability of the weld made.
Let’s take a closer look at what types of welding are frequently used in industry, how they are realised and their important role in the world.
4 different welding methods used in industry
- Shielded Metal Arc Welding, also known as Stick Welding
- Submerged Arc Welding
- Gas Tungsten Arc Welding (TIG)
- Gas Metal Arc Welding (GMAW/MIG-MAG)
Although not common, the following welding methods are also used in industry;
- Plasma Arc Welding
- Flux-Cored Arc Welding
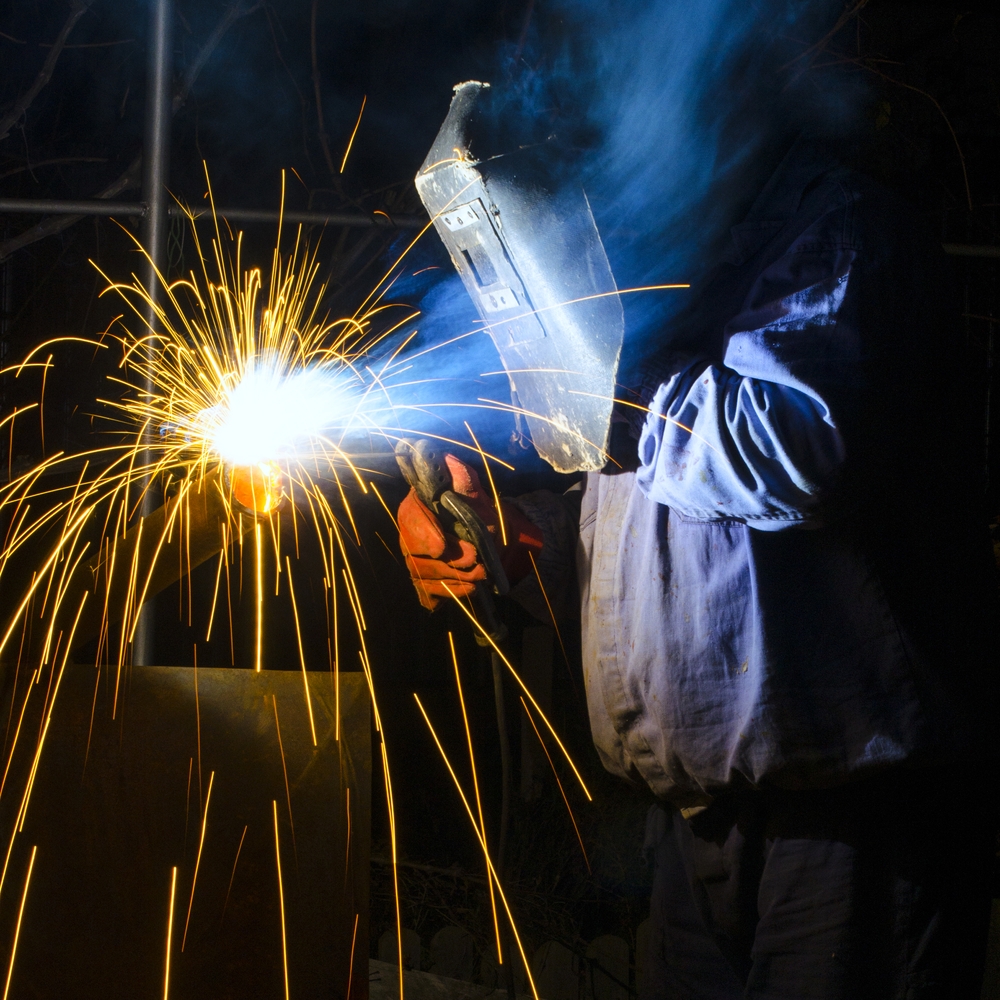

Let’s take a detailed look at each method.
- Shielded Metal Arc Welding: Shielded Metal Arc Welding (SMAW), also known as “electrode welding”, is a manual welding process. In this method, a metal electrode is brought close to the surface of the material to be welded. The electrode is melted by exposure to electric current during the welding process and drips onto the surface to be welded. A flux (coating) is used to protect the molten metal and electrode formed during the welding process. This flux protects the weld from the atmosphere, prevents oxidation and improves the weld quality. SMAW is generally a portable welding method that can be applied quickly. Due to these features, it is widely used in various industries, especially in building construction and maintenance-repair works.
- Submerged Arc Welding: Submerged arc welding, or SA welding for short, is a special welding method that uses an invisible electrode during the welding process. In this method, the welding arc and the weld pool are covered with a granular powder layer. This dust layer contains a kind of flux and protects the welding zone from environmental influences.
- Gas Tungsten Arc Welding: GTAW is a welding method also known as Tungsten Inert Gas (TIG) welding. In this method, a non-depleted tungsten electrode is used for the welding process. The electrode does not come into contact with the metal to be welded and does not melt. During the welding process, inert gases, typically argon or helium, protect the welding area from external influences. These gases prevent oxidation and ensure a clean welding process. Depending on the welding application, an additional filler metal may be required.
- Gas Metal Arc Welding: Gas Metal Arc Welding (GMAW), also known as MIG (metal inert gas), MAG (metal active gas). In this method, the wire electrode is advanced through a welding gun and this wire melts the base metal. As a result, a clean and durable weld joint is created.
- Plasma Arc Welding: Plasma welding is an advanced welding method that uses plasma, a high-temperature ionised gas, between the welding electrode and the workpiece. In this process, an inert gas (usually argon) is used to create a protective atmosphere in the welding area. This medium prevents oxygen from entering the weld zone from the air during the welding process. The plasma arc created between the electrode and the workpiece melts the metal by generating intense heat.
- Flux-Cored Arc Welding: Flux cored arc welding (FCAW) is known as a semi-automatic welding method and is similar to MIG welding. FCAW uses a continuous wire-fed electrode and a constant voltage power supply. In this process, the wire used acts as both electrode and filler metal and contains a flux. The flux in the inner part of the wire reacts to provide protection from the atmosphere when the welding arc is formed, thus forming slag to improve the quality of the weld.
These welding methods are various techniques used in industrial production. The choice of method is determined based on the type of material, its thickness, welding details, and process requirements.
If you need process equipment with the highest welding quality, you can contact us. As GEO Tekno & GEO Proses, you can purchase process equipment manufactured by our experienced team of engineers and staff at our factory located in Izmir Cigli AOSB. GEO’s motto is to build not only a customer-business relationship, but also a lasting business friendship by supporting you at every stage of purchase and maintenance.
For further information,
+90 232 459 49 09